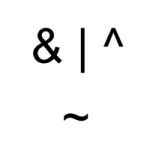 Bitwise operators are used in order to modify a bit or bits of any given byte.
Bitwise operators are used in order to modify a bit or bits of any given byte.
So whenever you want to modify less than a byte you can do it using this technique.
Using the bitwise operators you can save memory by packing multiple data items in a single byte.
Do not confuse the boolean operators AND(&&) OR(||) and NOT(!) with the bitwise operators AND(&) OR(|) NOT(~).
Let's start with the four most common bitwise operations : AND , OR , XOR and NOT.
| Operand 1 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 1 |
| Operand 2 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 1 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
| Result | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1 |
One of the most common uses of bitwise AND is to select a particular bit (or bits) from an integer value, often called masking.
Notice
0 AND X = 0
1 AND X = X
Let's see a simple masking technique
We have a single byte XXXXXXXX from this byte we want to read only the 2nd and third bit from the beginning. How can we do that ?
The answer is easy : XXXXXXXX AND 01100000 give as 0xx00000
| Operand 1 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 1 |
| Operand 2 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 1 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
| Result | 0 | 1 | 1 | 1 |
Notice
0 OR X = X
1 OR X = 1
Bitwise or is used to set high selected bits of a byte.
Lets see a use of the bitwise or. We want to make sure that the bits 2and 3 are high (1) and the others will remain unaltered.
XXXXXXXX OR 01100000 = X11XXXXX
There is an unusual operator in C++ called bitwise EXCLUSIVE OR
| Operand 1 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 1 |
| Operand 2 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 1 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
| Result | 0 | 1 | 1 | 0 |
Notice
X XOR X = 0
X XOR Y = 1 where X<>Y
X XOR 0 = X
X XOR 1 = NOT X
XOR is used to toggle selected bits from a byte (change from 0 to 1, or 1 to 0).
Example lets say again that we want to toggle only the 2nd and 3rd bit of a byte
XXXXXXXX XOR 01100000 = X(NOT X)(NOT X)XXXXXX
So use AND in order to do masking, use OR in order to set some bits high and finally use XOR in order to toggle selected bits